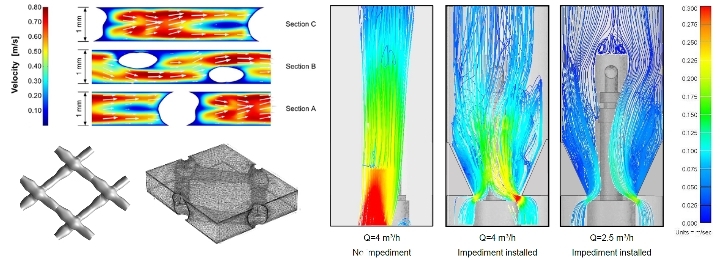
- Optimizing UVC-disinfection using LEDs as an energy efficient pre-treatment for biofouling control in spiral-wound membrane systems. Desalination 557, 2023, 116589 more…
- Inline dosing of powdered activated carbon and coagulant prior to ultrafiltration at pilot-scale – Effects on trace organic chemical removal and operational stability. Chemical Engineering Journal 414, 2021, 128801 more…
- Role of nanofiltration or reverse osmosis integrated to ultrafiltration-anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating vinasse for the conservation of water and nutrients in the ethanol industry. Journal of Water Process Engineering 36, 2020, 101338 more…
- A hydraulically optimized fluidized bed UF membrane reactor (FB-UF-MR) for direct treatment of raw municipal wastewater to enable water reclamation with integrated energy recovery. Separation and Purification Technology 235, 2020, 116165 more…
- Reducing the Impacts of Biofouling in RO Membrane Systems through In Situ Low Fluence Irradiation Employing UVC-LEDs. Membranes 10 (12), 2020, 415 more…
- Antibiotic microbial resistance (AMR) removal efficiencies by conventional and advanced wastewater treatment processes: A review. Science of The Total Environment 685, 2019, 596-608 more…
- CT scanning of membrane feed spacers – Impact of spacer model accuracy on hydrodynamic and solute transport modeling in membrane feed channels. Journal of Membrane Science 564, 2018, 133-145 more…
- A novel concept to integrate energy recovery into potable water reuse treatment schemes. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 2017, jwrd2017051 more…
- Seasonal variations in fate and removal of trace organic chemical contaminants while operating a full-scale membrane bioreactor. Science of The Total Environment 550, 2016, 176 - 183 more…
- Hazardous events in membrane bioreactors – Part 3: Impacts on microorganism log removal efficiencies. Journal of Membrane Science 497, 2016, 514-523 more…
- Mechanisms of Pathogenic Virus Removal in a Full-Scale Membrane Bioreactor. Environmental Science & Technology 49 (5), 2015, 2815-2822 more…
Membrane processes play a central role while establishing closed water cycles, for the reuse of municipal wastewater as well as in seawater desalination. The research of the Membrane Filtration group at the chair currently focuses on the suppression of biofouling by integrating UV-LEDs into membrane modules, the combination of powdered activated carbon and ozone with ceramic ultrafiltration membranes, the retention of microbial and chemical contaminants in highpressure membranes, as well as fouling mitigation strategies by alternative membrane surface patterns.
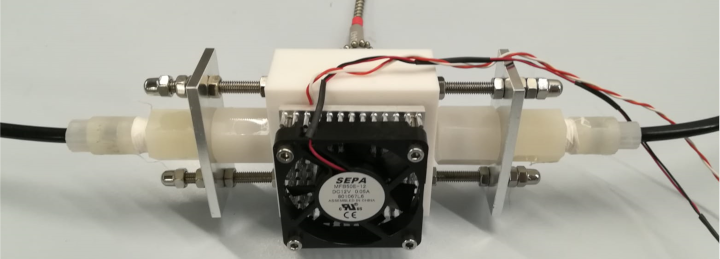
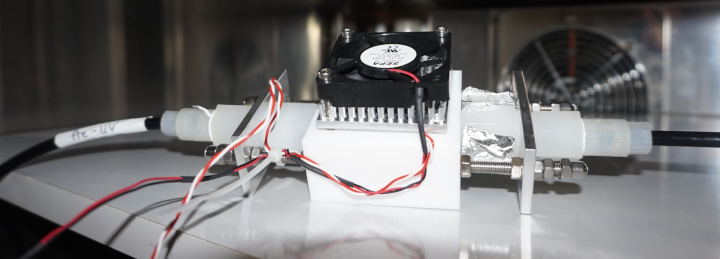
Since the end of 2018, we have been working in a BMBF project on the question of how far unwanted biofouling on the membrane, which affects the energetic efficiency of the membrane process, can be reduced. By using UV-C LEDs, we are developing UV-membrane hybrid processes in which targeted UV pretreatment delays the formation of biofouling and, at the same time, UV-induced effects in microorganisms to positively influence the properties of the formed biofilm in terms of its permeability and cleanability.
The coupling of powdered activated carbon with ultrafiltration membranes results in high efficiencies for the retention of microbial contaminants but also organic trace substances. In this context, the mechanisms of retention of antibiotic resistance carriers need to be clarified in more detail in order to ensure high effluent quality. Furthermore, the formation of cover layers has to be optimized in such a way that operational advantages result. These water qualities would allow reuse for urban and agricultural irrigation as well as artificial groundwater recharge.
In 2022, we have launched the new project FreeSpace in collaboration with the University of Duisburg-Essen funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) to investigate membrane fouling mitigation strategies by employing modified membrane surface patterns and new spacer configurations.